-
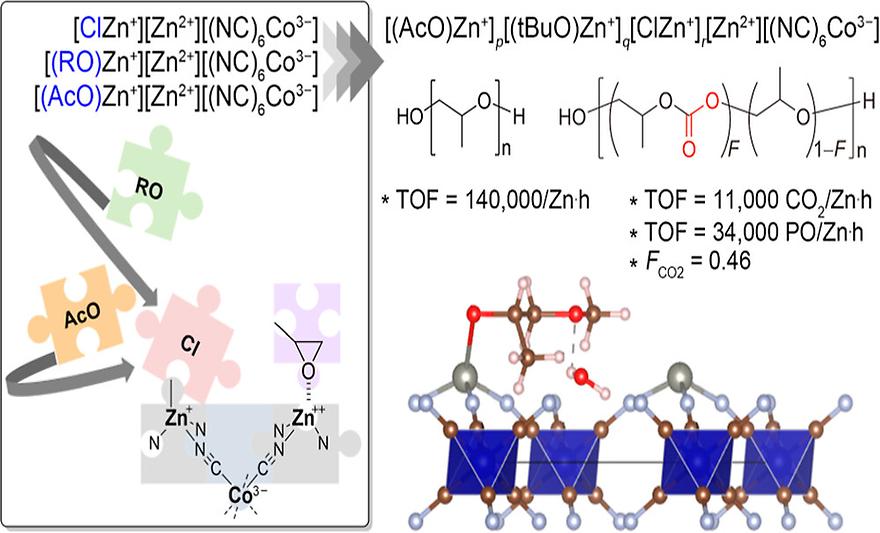
Graphene Oxides as Epsilon-Near-Zero Platforms Operating in Terahertz Frequency Rangeby Yeong Hyun Seo, Mi Ryu Lee, Da-Young Lee, Jun Hyeong Park, Hyeon Jeong Seo, Sang Uk Park, Hyunjin Kim, Seung-Joo Kim, Bun Yeoul LeeInorganic Chemistry 2024, 63(2), 1414–1426; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c03957AbstractReevaluating the composition of the double metal cyanide catalyst (DMC) as a salt of (NC)6Co3– anions with 1:1 Zn2+/(X)Zn+ cations (X = Cl, RO, AcO), we prepared a series of well-defined DMCs, [ClZn+][Zn2+][(NC)6Co3–][ROH], [(RO)Zn+][Zn2+][(NC)6Co3–], [(AcO)Zn+][Zn2+][(NC)6Co3–], [(RO)Zn+]p[ClZn+](1–p)[Zn2+][(NC)6Co3–], [(AcO)Zn+]p[(tBuO)Zn+]q[Zn2+][(NC)6Co3–], and [(AcO)Zn+]p[(tBuO)Zn+]q[ClZn+]r[Zn2+][(NC)6Co3–]. The structure of [(MeOC3H6O)Zn+][Zn2+][(NC)6Co3–] was precisely determined at the atomic level through Rietveld refinement of the synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction data. By evaluating the catalyst’s performance in both propylene oxide (PO) polymerization and PO/CO2 copolymerization, a correlation between structure and performance was established on various aspects including activity, dispersity, unsaturation level, and carbonate fraction in the resulting polyols. Ultimately, our study identified highly efficient catalysts that outperformed the state-of-the-art benchmark DMC not only in PO polymerization [DMC-(OAc/OtBu/Cl)(0.59/0.38/0.15)] but also in PO/CO2 copolymerization [DMC-(OAc/OtBu)(0.95/0.08)].Subjects: Animal feed; Catalysts; Diffraction; Layers; Polyols
-
82
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-28
- 203
- 동영상동영상
-
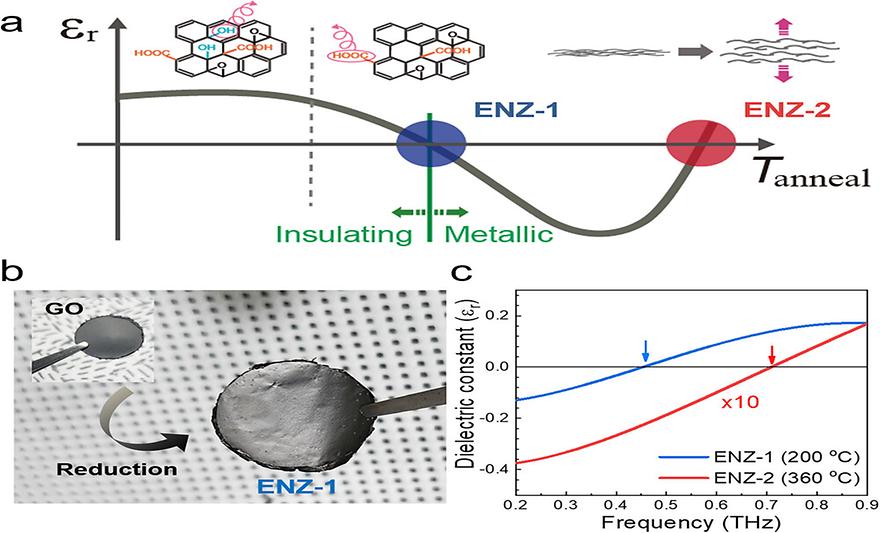
Graphene Oxides as Epsilon-Near-Zero Platforms Operating in Terahertz Frequency Rangeby Seung Won Jun, Jong Hyuk Yim, Ji-Yong Park, Soonil Lee, Yeong Hwan AhnLaser & Photonics Reviews 2024, 18(1), 2300726; https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.202300726AbstractEpsilon-near-zero (ENZ) materials, with their unique light manipulation capabilities, have fascinating applications such as cloaking, super-resolution imaging, energy harvesting, and sensing. Herein, free-standing graphene oxide films are fabricated whose dielectric constant can be engineered by thermal reduction, resulting in ENZ characteristics at the transition between insulating and metallic phases. The ENZ frequency is found to be 0.4–0.5 THz under an annealing temperature of 200 °C, whereas another ENZ phase appeared at 360 °C. ENZ film can be transferred to curved metal surfaces, serving as superabsorbers that suppress wave reflection from underneath metal surfaces. Hyper-resolution in nondestructive THz imaging is also possible, owing to superior beaming. Spatial resolution is improved two-fold by adding the ENZ film, even when the metal pattern is enclosed by a paint layer. Lastly, hybrid sensors are developed by incorporating the meta-pattern on the free-standing ENZ substrate. The energy splitting of metamaterial resonance originating from the coupling with ENZ mode is observed. Hybridized devices have proven effective in detecting microorganisms with a low refractive index, owing to the unique dielectric configuration offered by ENZ material. Using the novel ENZ platform, a 15-fold improvement in microbial sensitivity is achieved compared with the conventional sensors.
-
80
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-28
- 227
- 동영상동영상
-
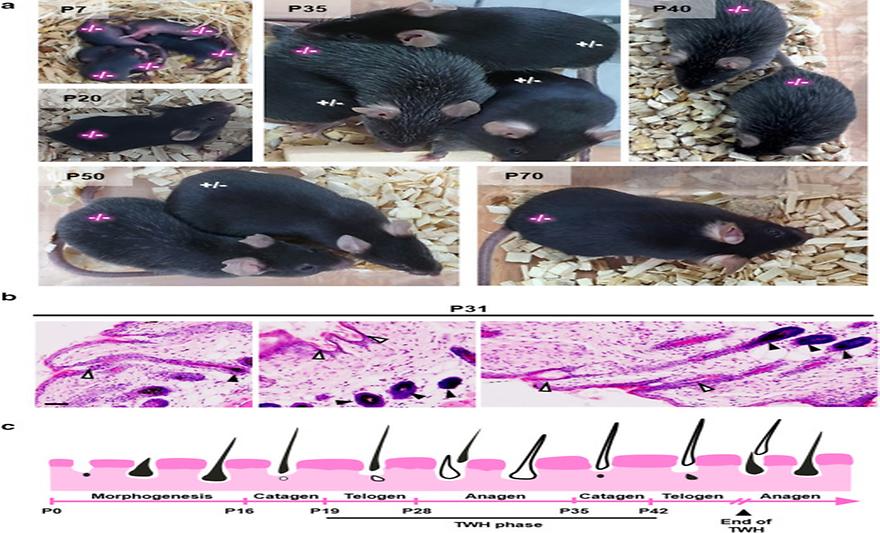
The Slc45a4 Gene Regulates Pigmentation in a Manner Distinct from that of the OCA4 Gene Slc45a2by Sofia Brito, Hyojin Heo, Byungsun Cha, Sang Hun Lee, Gunwoo Park, Byeong-Mun Kwak, Je Kyung Seong, Ho Lee, Ji-Hwan Park, Byung Mook Weon, Bum-Ho BinJournal of Investigative Dermatology 2024, 144(3), 720-722.e5; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2023.08.027In this study, we show that mouse Slc45a4 is also involved in pigmentation. By monitoring Slc45a4-knockout mice generated by CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing (Korea Mouse Phenotyping Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea) (Supplementary Figure S3a–c), we observed a distinctive phenotype consisting of a transient white hair period. This phase occurred specifically between postnatal days 20 and 70, corresponding to the first postnatal hair cycle, or the adolescence period in the case of C57BL/6J mice (Figure 1). Our observations revealed that, until postnatal day 20, Slc45a4-knockout mice had a fully black dorsal coat (Figure 1a). However, by postnatal day 35, a great portion of the dorsal coat was comprised of white hair. The white coat progressively faded along the cycle, starting from the head to the dorsal end, reducing significantly by postnatal day 49, and vanishing by postnatal day 70, corresponding to the second telogen step in C57BL/6J mice (Müller-Röver et al, 2001).
-
78
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-28
- 254
- 동영상동영상
-
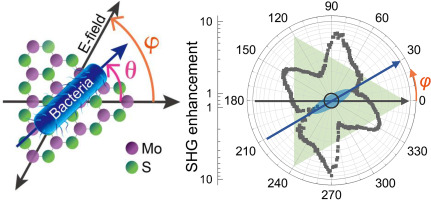
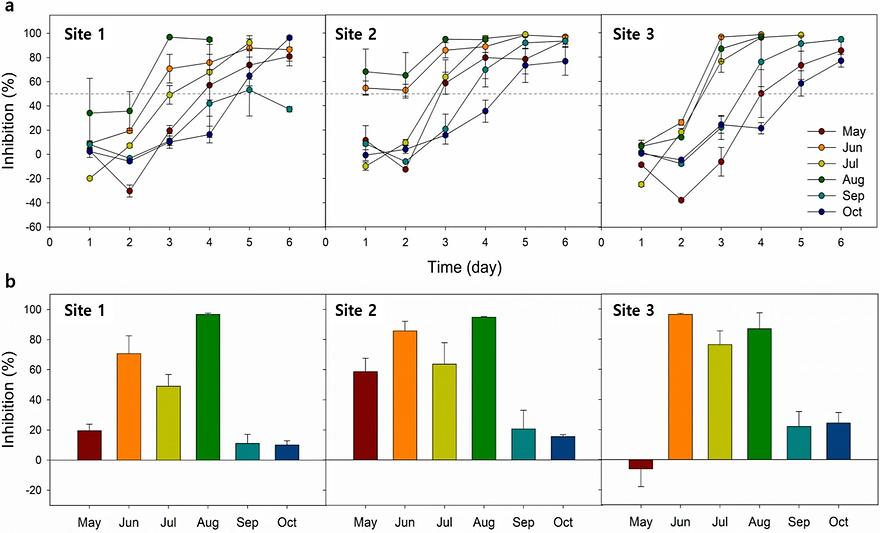
Single bacteria identification with second-harmonic generation in MoS2by Young Chul Kim, Seung Won Jun, Yeong Hwan AhnBiosensors and Bioelectronics 2023, 241, 115675; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2023.115675AbstractTransition-metal dichalcogenides exhibit extraordinary optical nonlinearities, making them promising candidates for advanced photonic applications. Here, we present the microbial control over second-harmonic generation (SHG) in monolayer MoS2 and the identification of single-cell bacteria. Bacteria deposited on monolayer MoS2 induce a change in the SHG signal, in the form of anisotropic polarization responses that depend on the relative orientation of the bacteria with respect to the MoS2 crystallographic direction. The anisotropic enhancement is consistent with the presence of a tensile stress along the lateral direction of bacteria axis; SHG imaging is highly effective in monitoring biomaterial strain as low as 0.1%. We also investigate the ultraviolet-induced removal of single bacteria, through the SHG imaging of MoS2. By monitoring the transient SHG signals, we determine the rupture times for bacteria, which varies noticeably for each species. This allows us to distinguish specific bacteria that share habitats; SHG imaging is useful for label free identification of pathogens at the single cell levels such as E. coli and L. casei. This label-free detection and identification of pathogens at the single-cell level can have a profound impact on the development of diagnostic tools for various applications.Keywords: Second harmonic generation; Transition metal dichalcogenides; Bacteria; Label-free sensing; Microbial strain
-
76
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-22
- 285
- 동영상동영상
-
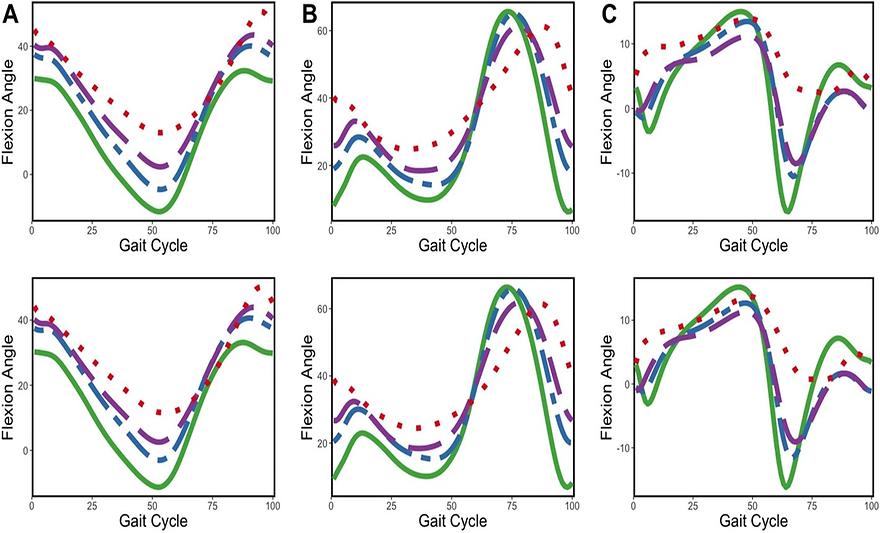
Interpretable classification for multivariate gait analysis of cerebral palsyby Changwon Yoon, Yongho Jeon, Hosik Choi, Soon-Sun Kwon & Jeongyoun AhnBioMedical Engineering OnLine 2023, 22, 109; https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-023-01168-xAbstractBackgroundThe Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) is a widely used tool for assessing the mobility of people with Cerebral Palsy (CP). It classifies patients into different levels based on their gross motor function and its level is typically determined through visual evaluation by a trained expert. Although gait analysis is commonly used in CP research, the functional aspects of gait patterns has yet to be fully exploited. By utilizing the gait patterns to predict GMFCS, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of how CP affects mobility and develop more effective interventions for CP patients.ResultIn this study, we propose a multivariate functional classification method to examine the relationship between kinematic gait measures and GMFCS levels in both normal individuals and CP patients with varying GMFCS levels. A sparse linear functional discrimination framework is utilized to achieve an interpretable prediction model. The method is generalized to handle multivariate functional data and multi-class classification. Our method offers competitive or improved prediction accuracy compared to state-of-the-art functional classification approaches and provides interpretable discriminant functions that can characterize the kinesiological progression of gait corresponding to higher GMFCS levels.ConclusionWe generalize the sparse functional linear discrimination framework to achieve interpretable classification of GMFCS levels using kinematic gait measures. The findings of this research will aid clinicians in diagnosing CP and assigning appropriate GMFCS levels in a more consistent, systematic, and scientifically supported manner.Keywords: Cerebral palsy; Functional sparse classification; GMFCS; Multivariate functional data; Sparse functional linear discriminant analysis
-
74
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-22
- 253
- 동영상동영상
-
-
72
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-22
- 292
- 동영상동영상
-
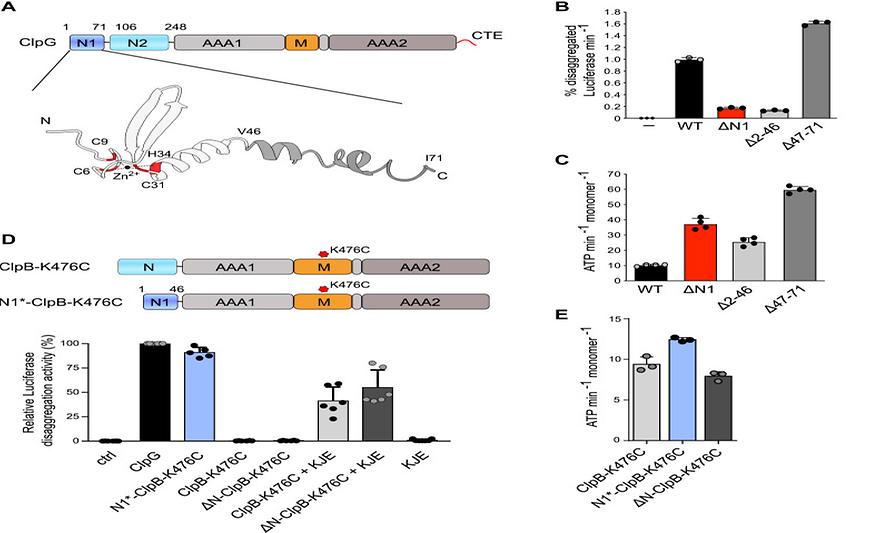
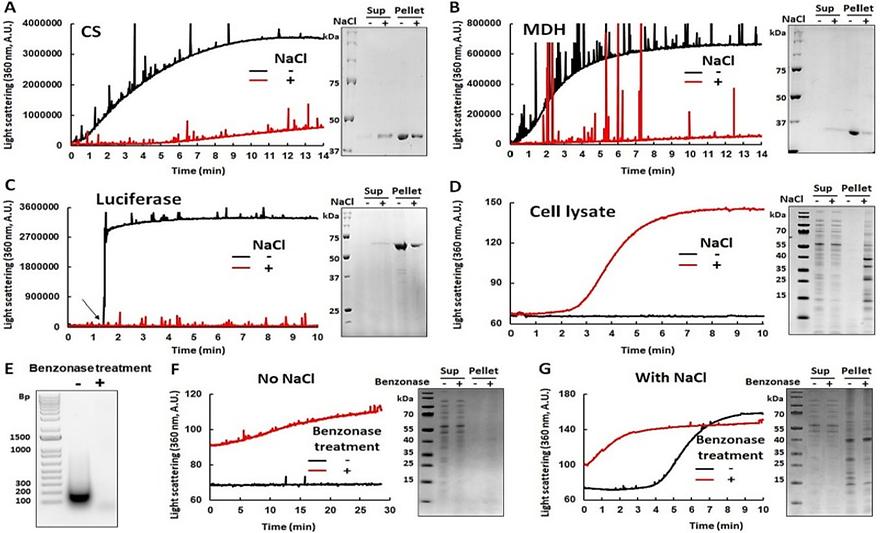
Structural basis of aggregate binding by the AAA+ disaggregase ClpGby Panagiotis Katikaridis, Bernd Simon, Timo Jenne, Seongjoon Moon, Changhan Lee, Janosch Hennig, Axel MogkJournal of Biological Chemistry 2023, 299(11), 105336; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105336AbstractWe demonstrate the generation and control of polaritonic states in perovskite phonon polaritons, which are strongly coupled in the middle of a flexible Fabry–Perot cavity. We fabricated flexible perovskite films on a microporous substrate coated with graphene oxide, which led to a virtually free-standing film incorporated into the microcavity. Rabi splitting was observed when the cavity resonance was in tune with that of the phonons. The Rabi splitting energy increased as the film thickness increased, reaching 1.9 meV, which is 2.4-fold higher than the criterion for the strong coupling regime. We obtained dispersion curves for various perovskite film thicknesses exhibiting two polariton branches; clear beats between the two polaritonic branches were observed in the time domain. Flexible cavity devices with perovskite phonons enable macroscopic control over the polaritonic energy states through bending processes, which add an additional degree of freedom in the manipulation of polaritonic devices.Keywords: ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities (AAA); protein aggregation; molecular chaperone; stress; 70 kDa heat shock protein (Hsp70)
-
70
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-22
- 297
- 동영상동영상
-
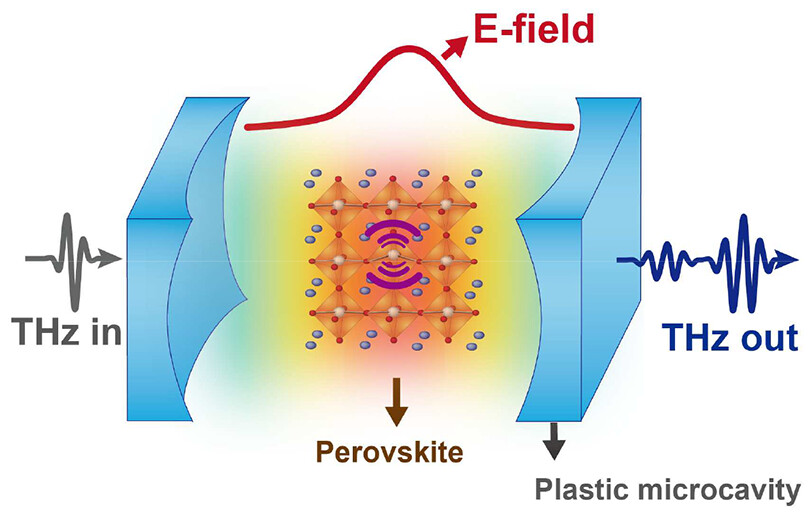
Mechanical Control of Polaritonic States in Lead Halide Perovskite Phonons Strongly Coupled in THz Microcavityby H. S. Kim, A. A. Khan, J.-Y. Park, S. Lee, and Y. H. AhnThe Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 2023, 14, 46, 10318–10327; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c02717AbstractWe demonstrate the generation and control of polaritonic states in perovskite phonon polaritons, which are strongly coupled in the middle of a flexible Fabry–Perot cavity. We fabricated flexible perovskite films on a microporous substrate coated with graphene oxide, which led to a virtually free-standing film incorporated into the microcavity. Rabi splitting was observed when the cavity resonance was in tune with that of the phonons. The Rabi splitting energy increased as the film thickness increased, reaching 1.9 meV, which is 2.4-fold higher than the criterion for the strong coupling regime. We obtained dispersion curves for various perovskite film thicknesses exhibiting two polariton branches; clear beats between the two polaritonic branches were observed in the time domain. Flexible cavity devices with perovskite phonons enable macroscopic control over the polaritonic energy states through bending processes, which add an additional degree of freedom in the manipulation of polaritonic devices.Keywords: Nucleic acids; DNA; RNA; Chaperone; Anti-aggregation activity
-
68
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-22
- 284
- 동영상동영상
-
-
66
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-22
- 252
- 동영상동영상
-
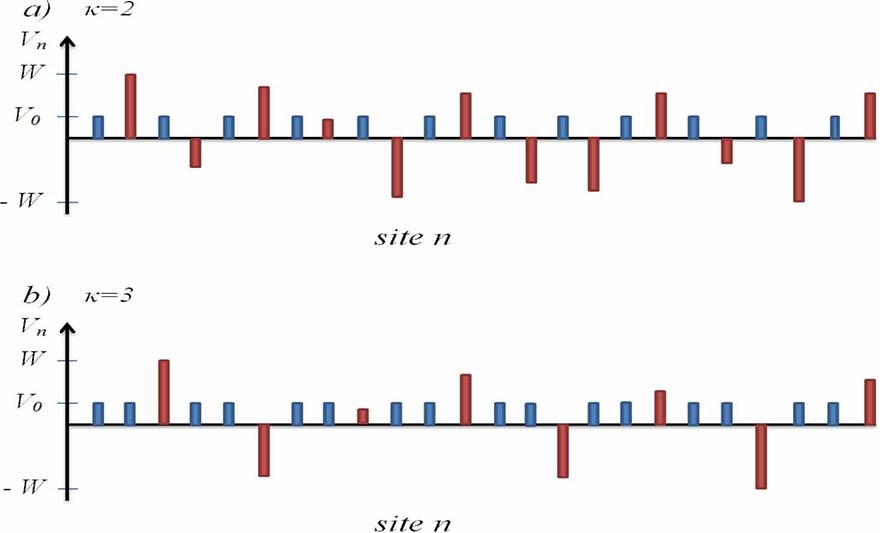
Transport and localization properties of excitations in one-dimensional lattices with diagonal disordered mosaic modulationsby Ba Phi Nguyen and Kihong KimJournal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical 2023, 56(47), 475701; https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8121/ad03cdAbstractWe present a numerical study of the transport and localization properties of excitations in one-dimensional lattices with diagonal disordered mosaic modulations. The model is characterized by the modulation period κ and the disorder strength W. We calculate the disorder averages 〈𝑇〉, 〈ln𝑇〉, and 〈𝑃〉, where T is the transmittance and P is the participation ratio, as a function of energy E and system size L, for different values of κ and W. For excitations at quasiresonance energies determined by κ, we find power-law scaling behaviors of the form 〈𝑇〉∝𝐿−𝛾𝑎, 〈ln𝑇〉≈−𝛾𝑔ln𝐿, and 〈𝑃〉∝𝐿𝛽, as L increases to a large value. In the strong disorder limit, the exponents are seen to saturate at the values 𝛾𝑎∼0.5, 𝛾𝑔∼1, and 𝛽∼0.3, regardless of the quasiresonance energy value. This behavior is in contrast to the exponential localization behavior occurring at all other energies. The appearance of sharp peaks in the participation ratio spectrum at quasiresonance energies provides additional evidence for the existence of an anomalous power-law localization phenomenon. The corresponding eigenstates demonstrate multifractal behavior and exhibit unique node structures. In addition, we investigate the time-dependent wave packet dynamics and calculate the mean square displacement 〈𝑚2(𝑡)〉, spatial probability distribution, participation number, and return probability. When the wave packet's initial momentum satisfies the quasiresonance condition, we observe a subdiffusive spreading of the wave packet, characterized by 〈𝑚2(𝑡)〉∝𝑡𝜂 where η is always less than 1. We also note the occurrence of partial localization at quasiresonance energies, as indicated by the saturation of the participation number and a nonzero value for the return probability at long times.
-
64
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-22
- 293
- 동영상동영상