-
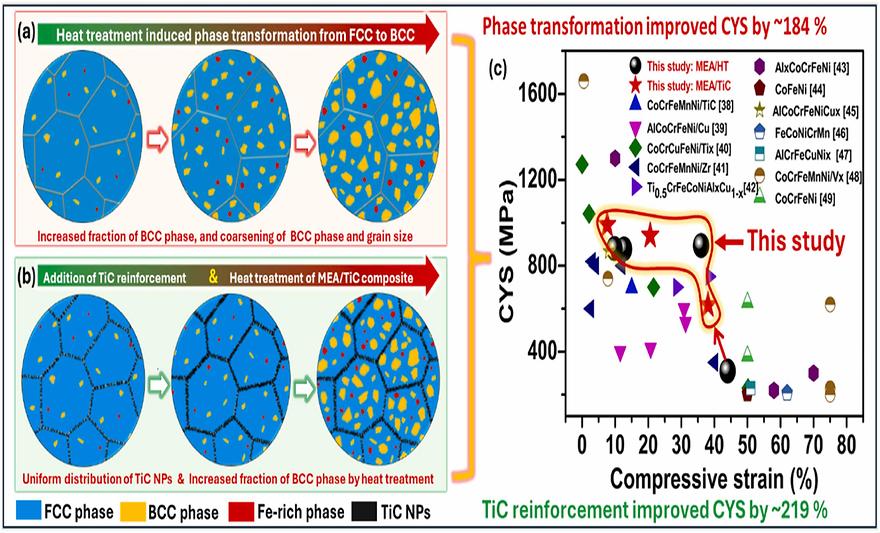
Strengthening of Fe60Co15Ni15Cr10 medium entropy alloy via heat-treatment-induced phase transformation and TiC reinforcementby Nagarjuna, Cheenepalli;Lee, Hansung;Dewangan, Sheetal Kumar;Song, Eunhyo;Mohan, Man;Jain, Reliance;Yu, Hwi Geun;Ahn, ByungminJournal of Alloys and Compounds 2025, 1020, 179453; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2025.179453AbstractThe ferrous-rich Fe60Co15Ni15Cr10 medium entropy alloy (MEA) was prepared via mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. To further enhance the strength of the MEA, the present study developed two effective strategies: optimizing the heat treatment temperature and incorporating TiC nanoparticles as a reinforcement phase. The obtained results revealed the formation of a single-phase face-centered cubic (FCC) structure within the MEA powder after 30 h of milling. While the MEA/TiC composite powder exhibited both FCC and TiC phases. After sintering, the predominant FCC phase and a minor CrFe-rich body-centered cubic (BCC) phase were observed. However, as the heat treatment temperature increased, a fraction of the BCC phase significantly increased. Consequently, the hardness of MEA increased by 54 % after heat treatment at 900 °C, while its compressive yield strength (CYS) increased by 184 % after heat treatment at 1000 °C. The addition of 5 wt.% TiC reinforcement improved its hardness and CYS by 47 % and approximately 219 %, respectively. Furthermore, heat-treatment-induced microstructural heterogeneity provides multiple stages of strain hardening. Hence, this study demonstrates that heat-treatment-induced phase transformation and TiC reinforcement can significantly enhance the strength and hardness of MEA, providing a viable approach to developing high-performance, cost-effective alloys for structural applications.Keywords: Medium entropy alloy; Phase transformation; Reinforcement; Microstructure; Mechanical behavior
-
126
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2026-01-30
- 19
- 동영상동영상
-
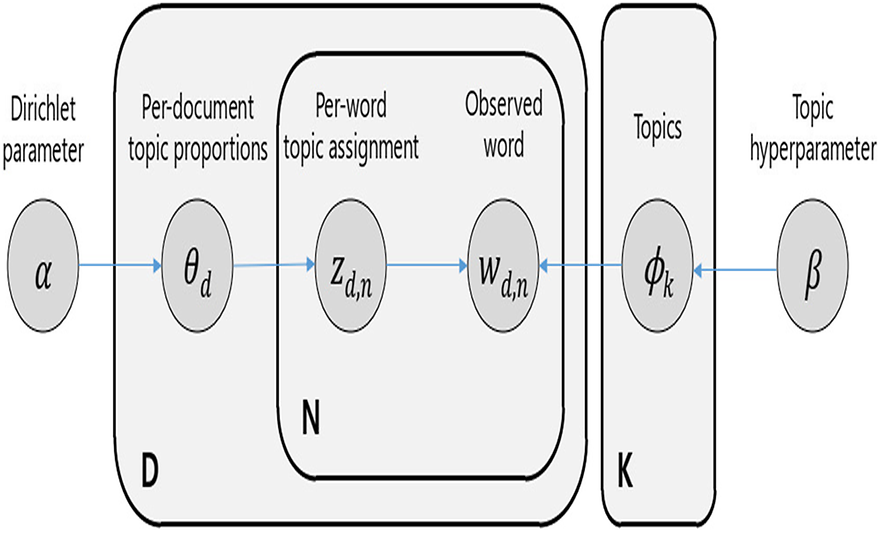
Visualization algorithm based on FDR control testing for dimension reduction of textual databy Sung-Inn Pyo; Soohyun Ahn; Soon-sun KwonData Technologies and Applications 2025, 59(2), 338-361; https://doi.org/10.1108/DTA-04-2024-0373PurposeVisualizing relations of textual data requires dimension reduction to increase the interpretability of output. However, traditional dimension reduction methods have some limitations, such as the loss of feature information during extraction or projection in dimension reduction and uncertain results due to the mixture of word labels. In this study, we develop the textual data visualization algorithm using statistical methods to present statistical inferences on the data. We also construct the algorithm in a way that the user can analyze textual data easily.Design/methodology/approachUnstructured data, such as textual data, is sensitive to choosing analysis methods. In addition, textual data is generally large-sized and sparse. Considering such characteristics, we applied latent Dirichlet allocation to separate data to minimize the loss of information, and false discover rate (FDR) control to reduce dimension in a statistical way.FindingsThe relation of textual data can be derived in a one-click way, and the output can be interpreted without background information, with separated topics.Originality/valueThe algorithm is constructed based on the Korean language. However, any language can be used without linguistic information. This study can be an example of usage and flow, which using not well-known dimension reduction methods can replace traditional methods.Keywords: Text mining, Semantic network, Visualization, Dimension reduction, False discovery rate control, Korean text data analysis
-
124
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2026-01-30
- 24
- 동영상동영상
-
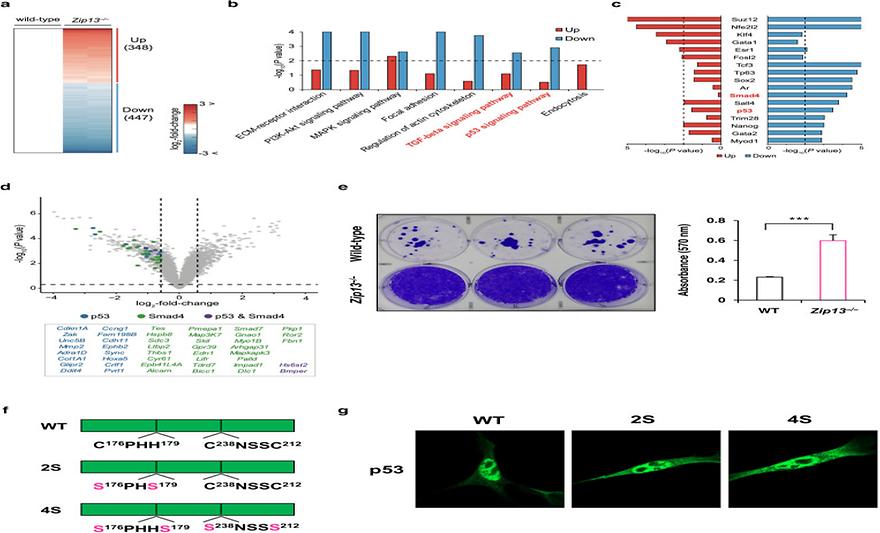
Zinc transporter ZIP13 G289R variant from Spondylocheirodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (SCD-EDS) is associated with hair qualityby Sofia Brito, Gang Hyoung Lee, Gunwoo Park, Valeria Capra, Gianmaria Viglizzo, Federico Zara, Jiyoon Kim, Sung Kweon Cho, Beat Steinmann, Irene Valenzuela, Andrea Superti-Furga, Ji-Hwan Park, Byung Mook Weon, Marcello Scala, and Bum-Ho BinJournal of Investigative Dermatology 2025, 145(9), 2327-2330; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2025.02.133To the EditorZinc is an important trace metal ion for skin and hair maintenance (Al-Khafaji et al, 2022; Bin et al, 2017). In this study, we identified a patient harboring the homozygous (NM_001128225.3): c.865G>C, p.(Gly289Arg) variant in the human SLC39A13 gene (Mendelian Inheritance in Man: 608735), encoding the Golgi apparatus zinc transporter ZIP13 (Supplementary Figure S1). This male aged 20 years was born to unaffected, reportedly unrelated parents of Italian ancestry, each carrying the variant in a heterozygous state. The patient is the only child born to the couple, and no other family members were reported to be affected. Biallelic loss-of-function variants in SLC39A13 have been linked to spondylocheirodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (SCD-EDS) (Mendelian Inheritance in Man: 612350), a condition characterized by a reduced fiber number and thickness in connective tissues (Bin et al, 2014; Giunta et al, 2008). Our patient displayed the classical SCD-EDS phenotype featuring facial dysmorphism, short neck, sloping shoulders, and kyphoscoliosis with diffuse rigidity. Both hands showed ulnar deviations, arachnodactyly, laxity of small joints, and palmar keratoderma. X-ray studies revealed long proximal phalanges in fingers and platyspondyly of dorsal vertebrae. Although most clinical reports of patients with SLC39A13-SCD-EDS indicate phenotypes associated with the skin or bones (Kumps et al, 2020), we observed abnormalities in hair quality in this patient (Figure 1a). For instance, the hairs located in the eyebrow region appeared sparse and thin (i in Figure 1a), and the popliteal region of the right leg (ii in Figure 1a) and the dorsal surface of the left arm (iii in Figure 1a) exhibited a notable absence and rarity of hair, respectively. In addition, a large area with a severe lack of hair could be observed in the left thigh (iv in Figure 1a). No abnormalities were detected in the scalp hair, making a diagnosis of alopecia areata unlikely. Although collagen dysgenesis–related symptoms are considered the primary features associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndromes, hair abnormalities have also been identified in SCD-EDS subtypes. Indeed, sparse scalp hair has been reported in patients with B4GALT7-SCD-EDS or B3GALT6-SCD-EDS, with variable prevalence (Brady et al, 2017; Caraffi et al, 2019). Hence, it is plausible that hair abnormalities could constitute a previously uncharacterized phenotypic feature of SLC39A13-SCD-EDS, this being a shared characteristic among distinct genetic subtypes of SCD-EDS.Keywords: Golgi apparatus; Hair; SLC39A13; Spondylocheirodysplastic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome; Zinc
-
122
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2026-01-30
- 22
- 동영상동영상
-
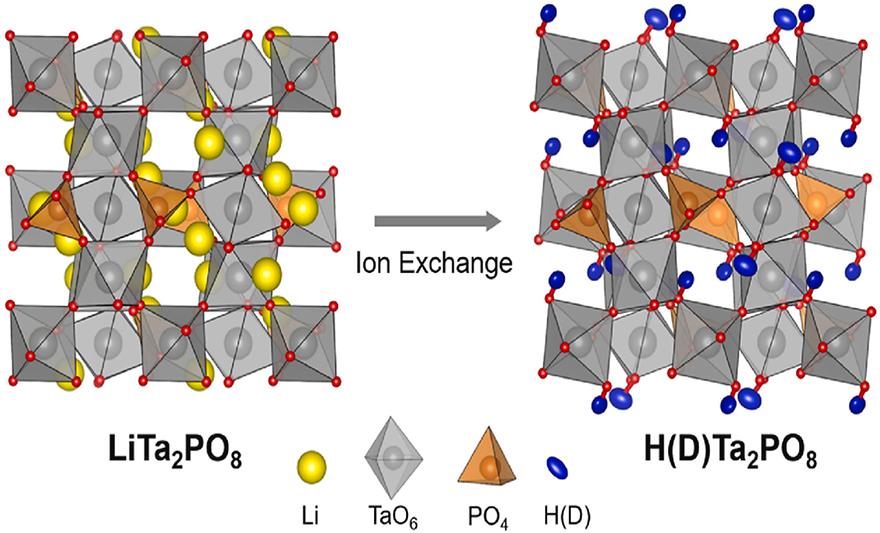
Crystal structure, thermal behavior, and proton conductivity of HTa2PO8 synthesized via ion-exchange from LiTa2PO8by Jaegyeom Kim; Fouzia Khefif; Heeyoun Kim; Ji-Sun Lee; Seongsu Lee; Chung-Yul Yoo; Seung-Joo KimJournal of Solid State Chemistry 2025, 346, 125278; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2025.125278AbstractA protonated/deuterated compound, HTa2PO8/DTa2PO8, was synthesized via an ion-exchange reaction of LiTa2PO8 in aqueous HCl/DCl solution. The structure was analyzed to clarify the location of the proton (or deuterium) in the lattice, using synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction (SXPD) and neutron powder diffraction (NPD). The crystal structure of DTa2PO8 belongs to the monoclinic space group, C2/c, identical to that of parent LiTa2PO8. The deuterium atoms were found to partially occupy two distinct sites around oxygen atoms, located at the shared corners of two connected TaO6 octahedra. The two distinctive H+ sites were confirmed by the solid-state 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrum of HTa2PO8. HTa2PO8 is thermally stable up to 400 °C, and as the temperature increases, it transforms into an intermediate compound, Ta2PO7.5, while maintaining its original framework structure. Above 1050 °C, it subsequently decomposes to Ta2O5 and TaPO5. Impedance spectroscopy measurements, performed in both dry and wet air, showed that HTa2PO8 exhibited an ion conductivity ranging from 10−5 to 10−8 S/cm in the temperature range of 200 °C∼400 °C, in which protons are the primary charge carriers.Keywords: Ion exchange; Neutron diffraction; Crystal structure; Thermal stability; Ionic conductivity
-
120
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2026-01-30
- 21
- 동영상동영상
-
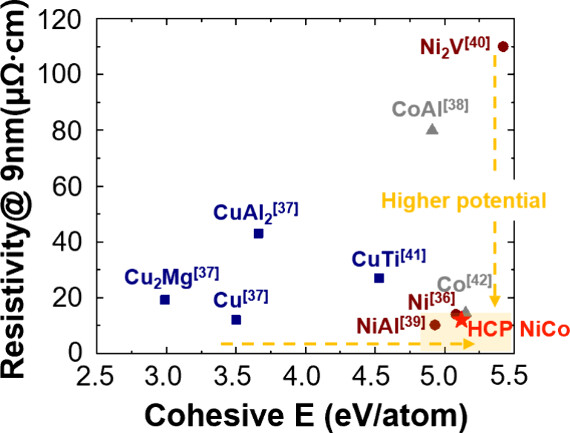
Demonstration of NiCo as an Alternative Metal for Post-Cu Interconnectsby Ju Young Sung, Gi-Young Jo, Sang Mo Moon, Chae Hyun Lee, Yebin Lim, Yewon Yun, Sang Hyuk Lee, Jeong-Yub Lee, Dae-Jin Yang, Sang Won Kim, Sang Woon LeeACS Nano 2025, 19(7), 7253-7262; https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.4c17216AbstractCopper (Cu) is currently the dominant interconnect material in back-end-of-line processes due to its low bulk resistivity (ρ0). Unfortunately, its resistivity increases significantly at small dimensions due to a long electron mean free path (EMFP, λ) of 39 nm, which leads to enhanced electron scattering at grain boundaries and surfaces, thereby limiting high-density integration. In this study, we demonstrate that single-phase hexagonal-close-packed (HCP) nickel–cobalt (NiCo) alloy thin films exhibit a significantly reduced resistivity size effect, outperforming Cu interconnect material for thicknesses below 8 nm (19.83 μΩ·cm at 4.9 nm). First-principles calculations predicted a lower ρ0·λ of 5.68 × 10–16 Ω m2 for HCP NiCo (xx) than to Cu (6.73 × 10–16 Ω m2), due to a significant contribution from the short EMFP of approximately 5 nm in the HCP NiCo alloy. To date, the growth of single-phase HCP NiCo film had not been achieved, as both HCP and face-centered-cubic (FCC) phases coexist at Co concentration of 50–80 atom %. However, single-phase HCP NiCo films were successfully grown by using an HCP Co seed layer, which reduced the lattice mismatch with the sapphire (0001) substrate. Moreover, NiCo thin films can be successfully dry etched, providing a significant advantage in device fabrication, since it does not require a damascene process unlike Cu. The NiCo thin films also exhibited high thermal stability above 500 °C. Therefore, HCP NiCo is considered a promising alternative to overcome the scaling limitations of Cu interconnects.Keywords: metal thin film; NiCo; HCP; resistivity; size effect
-
118
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2026-01-30
- 18
- 동영상동영상
-
A Comprehensive Review on Hot Deformation Behavior of High-Entropy Alloys for High Temperature Applicationsby Jain, Reliance;Jain, Sandeep;Nagarjuna, Cheenepalli;Samal, Sumanta;Rananavare, Anuja P;Dewangan, Sheetal Kumar;Ahn, ByungminMetals and Materials International 2025, 31(8), 2181-2213; https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-024-01888-2AbstractIn contrast to conventional alloys, multicomponent high-entropy alloys (HEAs) have emerged as promising candidates in the field of advanced materials because of their unique composition, microstructure, mechanical and thermal properties, rendering these materials well-suited for a diverse range of applications. For high temperature applications, understanding the hot workability of HEAs is essential for optimizing their processing conditions, tailoring their microstructures and mechanical properties. The current review provides a comprehensive overview of the hot workability of HEAs, including the compression phenomenon observed during hot deformation, the application and use of processing maps, modeling approaches for predicting flow stress, and the deformation mechanisms involved. Different design strategies applicable to HEAs for high-temperature applications have been discussed in this review. The prediction of hot deformation behaviors and processing maps of different HEAs can benefit the research community in designing and developing HEAs for high-temperature applications. Furthermore, we highlight the future scope and challenges in this field.Subjects: High Temperature Plasma; Materials MechanicsMetals and Alloys; Molecular Deformation Dynamics; Phase Transitions and Multiphase Systems; Materials Engineering
-
116
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2026-01-30
- 14
- 동영상동영상
-
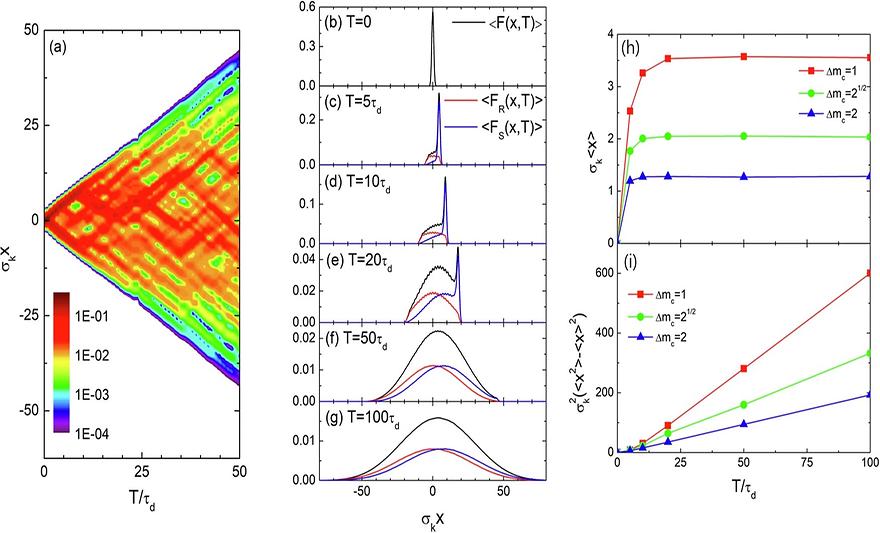
Spatial localization and diffusion of Dirac particles and waves induced by random temporal medium variationsby Kim, Seulong;Kim, KihongCommunications Physics 2025, 8, 32; https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-025-01951-3 AbstractWave propagation in time-varying media has attracted significant attention for its innovative potential to control wave-matter interactions and to develop versatile active materials. While most research has focused on electromagnetic waves, studies on Dirac-type waves remain limited. In this work, we investigate temporal scattering in pseudospin-1/2 Dirac systems with random temporal mass variations. Using the invariant imbedding method, we derive exact expressions for temporal reflectance in both short- and long-time regimes. In the long-time limit, reflectance probabilities become uniformly distributed, and wave group velocities decay to zero, indicating spatial localization. Numerical simulations reveal that narrow wave pulses evolve into Gaussian shapes, with their centers localizing and their widths growing indefinitely due to diffusive behavior. This universal phenomenon is independent of the initial pulse profile and the statistical properties of the random mass. Our findings demonstrate that random temporal variations can induce insulating behavior in Dirac materials, offering potential applications in solid-state physics and optics.Subjects: Metamaterials; Nanophotonics and plasmonics; Topological matter
-
114
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2026-01-30
- 22
- 동영상동영상
-
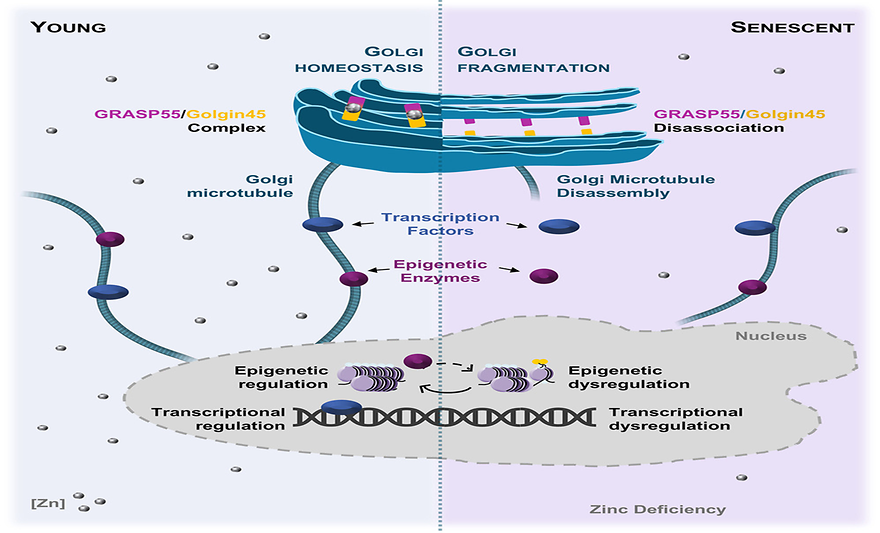
Age-associated interplay between zinc deficiency and Golgi stress hinders microtubule-dependent cellular signaling and epigenetic controlby Sofia Brito, Hyojin Heo, Jinyoung Kim, Byungsun Cha, Youngdo Jeong, Wooseon Choi, Chandani Shrestha, Gang Hyoung Lee, Sun Ju Park, Ki Bok Yoon, Kentaro Oh-hashi, Sung Tae Kim, Sehyun Chae, Sung Kweon Cho, Byung Mook Weon, Jiyoon Kim, and Bum-Ho BinDevelopmental Cell 2025, 60(9), 1304-1320; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2024.12.024SummaryGolgi abnormalities have been linked to aging and age-related diseases, yet the underlying causes and functional consequences remain poorly understood. This study identifies the interaction between age-associated zinc deficiency and Golgi stress as a critical factor in cellular aging. Senescent Golgi bodies from human fibroblasts show a fragmented Golgi structure, associated with a decreased interaction of the zinc-dependent Golgi-stacking protein complex Golgin45-GRASP55. Golgi stress is increased, and functions such as glycosylation and vesicle transport are impaired. These disturbances promote Golgi and perinuclear microtubule disassembly and subsequent mislocalization of intracellular proteins associated with cellular signaling and epigenetic control. Pharmacological induction of Golgi stress or zinc deficiency, or ablation of the Golgi-associated zinc transporter gene Zip13 in mouse fibroblasts, replicate the characteristics of cellular senescence, emphasizing the critical role of Golgi-zinc homeostasis. These findings highlight the importance of adequate zinc intake and suggest targeting Golgi dysfunction as a therapeutic strategy for alleviating age-related cellular decline.Keywords: aging; senescence; Golgi; zinc; zinc transporter; microtubules; signaling; epigenetics; ZIP13; GRASP55
-
112
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2026-01-30
- 25
- 동영상동영상
-
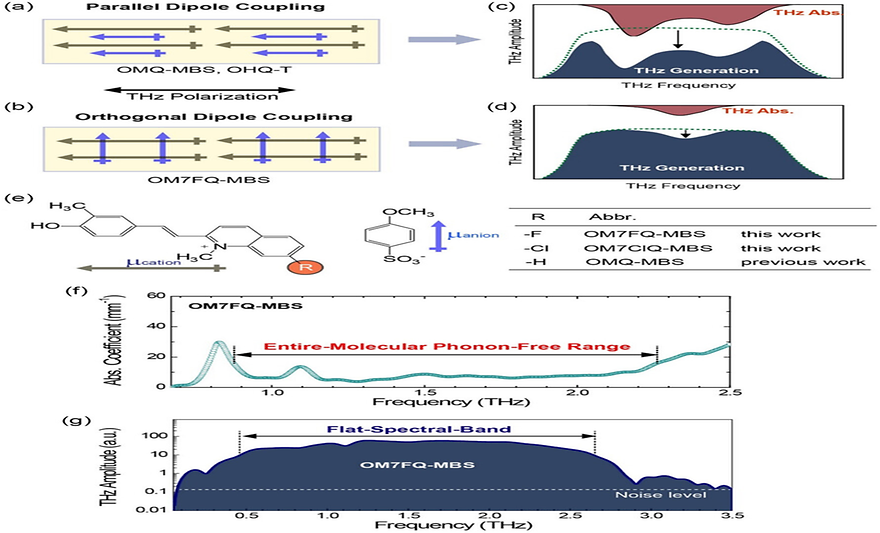
Organic Terahertz Generators with Wide Entire-Molecular Phonon-Free Range and Their Application in Broadband Terahertz Spectroscopyby Yun‐Sang Lee, Chaeyoon Kim, Jungkwon Oh, Woojin Yoon, Hoseop Yun, Mojca Jazbinsek, Fabian Rotermund, O‐Pil KwonSmall Structures 2025, 6(5), 2400483; https://doi.org/10.1002/sstr.202400483AbstractNew organic nonlinear optical crystals with a broad range free from strong molecular phonon vibrations have been developed for dimple-free THz wave generation. The newly designed 7-fluoro-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methylstyryl)-1-methylquinolin-1-ium (OM7FQ) crystals exhibiting an optimal order parameter feature a unique orthogonal cation–anion dipole coupling, in contrast to the parallel cation–anion dipole coupling found in benchmark organic crystals. The introduction of a fluoro substituent on the cationic electron acceptor, compared to nonfluorinated analogs, results in the additional formation of stronger cation–anion and cation–cation interactions, leading to increased crystal density and reduced void volume. OM7FQ single crystals exhibit a broad phonon-free range from 0.9 to 2.3 THz, defined by an absorption coefficient ≤15 mm−1. This leads to efficient, dimple-free THz wave generation with a dimple-free flat spectral band spanning 0.5–2.7 THz when pumped at the technically significant wavelength of 800 nm. Additionally, OM7FQ crystals produce THz electric fields 3.6 times higher than analogous nonfluorinated benchmark crystals with parallel cation–anion dipole coupling. The application of OM7FQ crystals in broadband THz spectroscopy has been successfully demonstrated for sensing biologically important lactose in commercial infant formulas.Keywords: nonlinear optics; organic crystals; terahertz spectroscopy; terahertz waves
-
110
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2026-01-30
- 20
- 동영상동영상
-
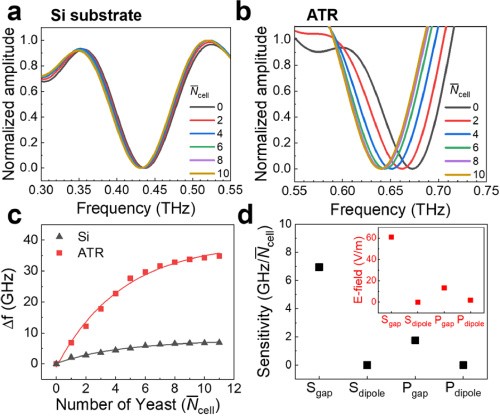
Terahertz metamaterial-prism hybrid sensors for the detection of microorganismsby Kim, Y. C.;Jun, S. W.;Park, S. J.;Ahn, Y. H.Optics Express 2024, 32(27), 48915-48924; https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.545112AbstractIn this study, we developed terahertz (THz) metamaterial devices with attenuated total reflection (ATR) geometries for biosensing applications. This was achieved by transferring the metamaterial patterns fabricated on a polyimide film to a prism-top surface. We characterized the resonance characteristics of metasurfaces for different THz wave polarizations and gap structure orientations in the metamaterials. The metamaterial resonances exhibited a sharp resonance compared to the normal incidence case; the quality factor increased from 3.3 to 6.0. For biosensing applications, we measured the resonant-frequency shift of the hybrid device by depositing yeast cells. The sensitivity in terms of the yeast number density increased 3.4 times compared to that of the Si substrate under normal incidence, which presented a 4.1-fold increase in the figure of merit. The resonance characteristics based on finite-difference time-domain simulations successfully reproduced our experimental results, including the enhanced sensitivity of our hybrid devices.
-
108
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2025-02-28
- 21
- 동영상동영상